In PowerShell, being able to execute scripts depends on the execution policy of your machine.
You might be able to change the execution policy yourself and set it to Unrestricted, meaning you can execute scripts without signing them.
If you are not an administrator, or your group policy defines the execution policy, you will need to sign your script.
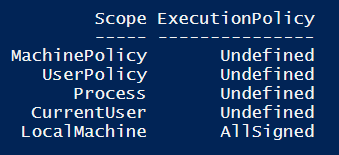
To see your current execution policy, execute the following command:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
To create a self-signed code signing certificate for PowerShell, makecert used to be the best solution.
In PowerShell we have a cmdlet called New-SelfSignedCertificate which we can also use for this purpose. Since V5 this cmdlet has been updated to make it easier to do so.
To create a Code Signing certificate execute the following command:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation
Cert:\CurrentUser\My -Type CodeSigningCert -Subject "U2U Code Signing"
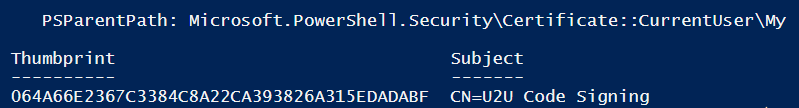
To verify that the certificate has been generated, run this command:
Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\CurrentUser\My | ? Subject -EQ "CN=U2U Code Signing"
The result should look like this.
Great! Now use the certificate to sign your script:
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath .\signedscript.ps1 -Certificate $cert
Oops! That didn't work!
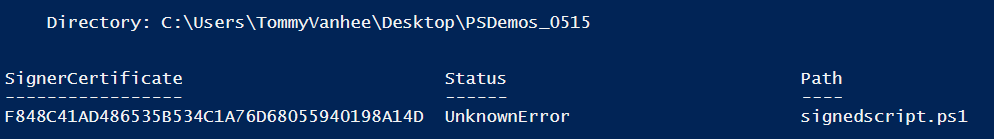
Our certificate is not trusted as it is in the personal store.
Let's move it to a better location:
Move-Item -Path $cert.PSPath -Destination "Cert:\CurrentUser\Root"
Make sure you confirm the installation of the certificate.
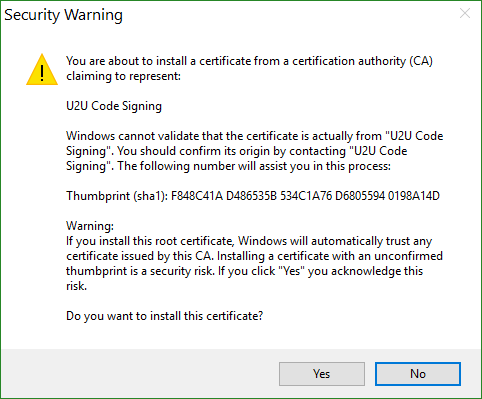
Now try again!
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath .\signedscript.ps1 -Certificate $cert
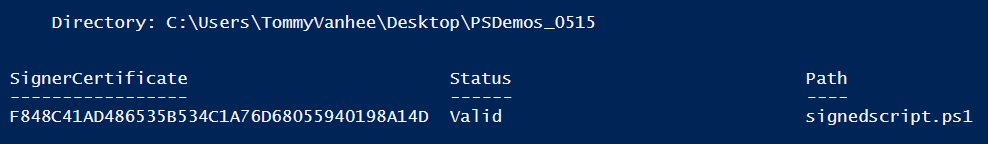
Better!
You should now be able to execute the signed script!
The full script looks like this:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\CurrentUser\My -Type CodeSigningCert -Subject "U2U Code Signing"
Move-Item -Path $cert.PSPath -Destination "Cert:\CurrentUser\Root"
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath .\signedscript.ps1 -Certificate $cert